Lifestyle
Orangutans Eat? Inside the Complex Diet of the Rainforest’s Most Intelligent Primate

Orangutans, the largest tree-dwelling mammals in the world, have long fascinated scientists and nature lovers alike. One of the most commonly asked questions is: What do orangutans eat? The answer reveals not just their diet but also their intelligence, survival strategies, and the fragility of their rainforest habitat.
This article explores the natural eating habits of orangutans, how their diet varies by species and region, and how human activities threaten their food sources.
Understanding the Orangutan Diet: A Fruit-Filled Lifestyle
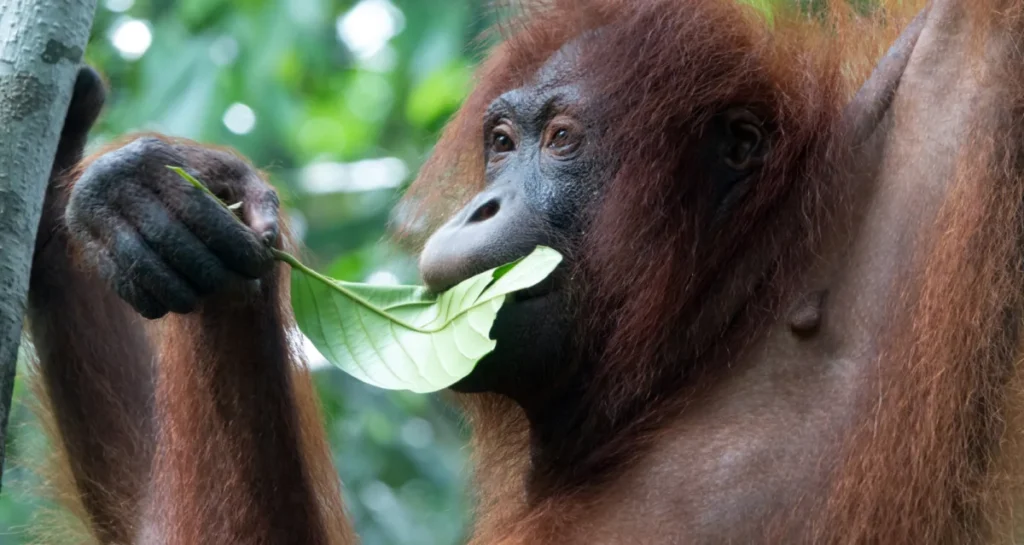

Orangutans are primarily frugivores, meaning they mainly eat fruit. In fact, fruit makes up about 60% to 90% of their natural diet, depending on the season and availability. Their favorite food includes:
- Figs
- Durian (a spiky fruit with a strong smell)
- Jackfruit
- Mangosteens
- Lychees
But these great apes don’t just eat fruit—they also consume other foods to meet their nutritional needs.
Secondary Foods Orangutans Eat
When fruit is scarce, orangutans turn to alternative food sources such as:
- Leaves and shoots – These are rich in fiber and help digestion.
- Bark – A backup food during dry seasons.
- Flowers – Especially from fig trees.
- Insects – Termites and ants are small protein-packed snacks.
- Honey and bird eggs – Rare but high-value foods.
- Soil and clay – To obtain minerals and neutralize toxins from certain plants.
This diverse diet showcases how adaptable orangutans are in their natural habitat.
Differences Between Bornean and Sumatran Orangutan Diets
There are three species of orangutans: Bornean, Sumatran, and the recently discovered Tapanuli orangutan. Their diets differ slightly based on location:
- Sumatran orangutans eat more insects and have access to more fruit year-round.
- Bornean orangutans face more frequent fruit shortages and eat more bark and leaves.
- Tapanuli orangutans, the rarest, have been observed eating insects, fruits, and even small vertebrates.
How Orangutans Forage for Food
Foraging takes up a major part of an orangutan’s day. These intelligent primates use:
- Memory – To remember fruiting trees and seasonal cycles.
- Tools – Sticks to extract honey, insects, or seeds.
- Social learning – Young orangutans learn what’s safe to eat by watching their mothers.
They typically travel alone or in small groups, which reduces competition for food.
Why Their Diet Matters for the Ecosystem
Orangutans are “gardeners of the forest.” As they eat fruit, they scatter seeds across wide areas through their droppings. This seed dispersal helps maintain rainforest biodiversity.
Without orangutans, many tree species could struggle to regenerate. That’s why preserving their diet is key to preserving the rainforest.
Impact of Habitat Loss on What Orangutans Eat
Unfortunately, orangutans are critically endangered, and deforestation is one of the biggest threats to their survival. As their natural habitat shrinks:
- Fruit-bearing trees disappear
- Food scarcity increases
- They are forced to raid crops, leading to conflict with humans
Palm oil plantations are a major driver of deforestation in Indonesia and Malaysia—regions home to all orangutan species.
What Do Orangutans Eat in Captivity?
In zoos or rehabilitation centers, orangutans are fed a carefully controlled diet that mimics their wild diet as closely as possible. This includes:
- A wide variety of fruits
- Vegetables like sweet potatoes and carrots
- Boiled eggs (for protein)
- Occasional nuts and seeds
Zookeepers avoid processed food to keep them healthy and prevent obesity.
Fun Facts About Orangutan Eating Habits
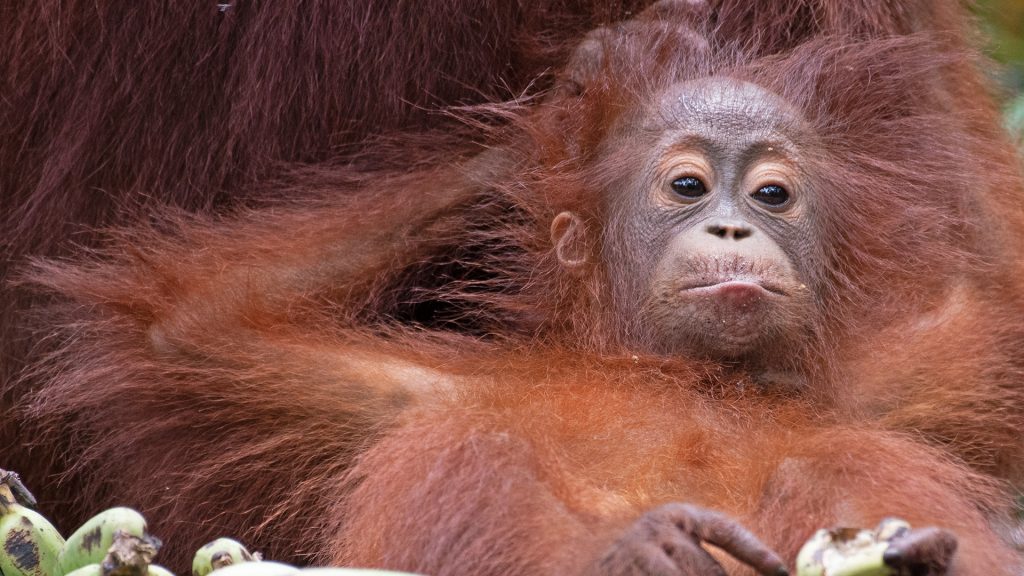

- Orangutans can open hard-shelled fruits like durian without tools.
- They chew leaves into a sponge to soak up water.
- They are one of the few non-human animals known to use leaf gloves when handling spiny or sticky fruits.
FAQs About What Orangutans Eat
Do orangutans eat meat?
Very rarely. Orangutans have been observed eating small animals or bird eggs, but it’s not a major part of their diet.
Can orangutans survive without fruit?
Temporarily, yes. During fruit shortages, they rely on bark, leaves, and insects, but long-term fruit scarcity can harm their health and reproduction.
Do baby orangutans eat the same things as adults?
Mostly. They nurse from their mothers for the first few years but start sampling solid foods by watching and copying their mothers.
Why do orangutans eat soil or clay?
To obtain minerals and to counteract toxins from unripe or bitter fruits.
Are orangutans picky eaters?
Not exactly. They prefer ripe fruit but are highly adaptable depending on availability.
Conclusion: Protecting the Orangutan’s Diet is Protecting Their Future
Understanding what orangutans eat is more than just curiosity—it’s essential for conservation. Their fruit-rich, diverse diet keeps them healthy and plays a critical role in the ecosystem.
But with rainforests vanishing fast, their survival is at stake.
If we want orangutans to continue thriving, we must protect their habitats, stop illegal logging, and support sustainable palm oil production.
Take action today—support organizations that protect orangutans and the forests they call home. Every choice we make, from what we buy to what we share, can help preserve one of the most intelligent and gentle creatures on Earth.